Fortigate Best practices – CLI Examples (7.0)
View the Fortigate best practices for 7.6 –> HERE
Management
*Missing from this guide.
- Management users from central user database ( LDAP, SAML etc )
Configure the web management ports
Hostname and the Alias of the firewalls.
I enable LLDP for easier debug on switches.
*Remember to change the values to match your desired naming scheme
config system global
set admin-port 8080
set admin-scp enable
set admin-sport 4443
set admintimeout 30
set alias "FortiGate-1800F"
set hostname "FGT1800F"
set lldp-reception enable
set lldp-transmission enable
set timezone 20
endCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Limit the management users to only login from specific ip addresses or subnets. Do not leave the management completely open.
This example also handles the backup user for the firewall, which will be readonly admin user
*Remember to change the values to match your desired naming scheme
config system admin
edit "admin"
set trusthost1 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0
set accprofile "super_admin"
set password XXXXXXXXXX
next
edit "backup_user"
set trusthost1 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255
set accprofile "super_admin_readonly"
set vdom "root"
set password XXXXXXXXXX
next
endCode language: CSS (css)If there are any automations needed through the API, create and limit the api user for the needed subnets and permissions
*Remember to change the values to match your desired naming scheme
config system api-user
edit "apiuser"
set api-key XXXXXX
set accprofile "API_Profile"
set vdom "root"
config trusthost
edit 1
set ipv4-trusthost 192.168.188.0 255.255.255.0
next
end
next
endCode language: CSS (css)Configure DNS, so the fortigate can reach the fortiguard servers and you can use FQDN for firewall policies, NTP Servers and more.
config system dns
set primary 1.1.1.1
set secondary 8.8.8.8
set protocol cleartext dot doh
set server-hostname "globalsdns.fortinet.net"
set domain "fgt1800.local"
endCode language: CSS (css)Configure NTP so the time are aligned with the rest of the network and so the timestamps in the logs are aligned with the real-world.
In this case the fortigate will also act as a NTP Server for the interfaces internal1 and internal2
config system ntp
set ntpsync enable
set type custom
set syncinterval 60
config ntpserver
edit 1
set server "dk.pool.ntp.org"
set ntpv3 disable
set authentication disable
set interface-select-method auto
next
end
set source-ip 0.0.0.0
set source-ip6 ::
set server-mode enable
set authentication disable
set interface "internal1" "internal2"
endCode language: JavaScript (javascript)High-Availability
In the HA config, the group-id is very important if you have multiple fortigate clusters on the same L2 network.
Otherwise the fortigates will conflict its HA virtual MAC address with a different HA cluster.
Example:
There are FortiGates SanFran, NewY, LA, and LasV.
FortiGate SanFran and NewY joined as HA1 (SanFran is Active)
FortiGate LA and LasV joined as HA2 (LA is Active)
The problem that occurs is that units SanFran and LA from different HA groups have the same virtual MAC address.
To fix this issue, consider changing the group ID of HA1 and HA2 to be different by changing the group-id to be another.
The Config must be identical on all cluster nodes, except the priority if you want to decide which fortigate that should be active.
The set override enable command does the same at preempt in a cisco hsrp config.
I recommend to have a dedicated interface for one of the management interfaces.
This allows for monitoring of the single cluster member so an error on the slave will be picked up before the fail-over was planned to happen.
config system ha
set group-id 0
set group-name "clu01"
set mode a-p
set password XXXX
set hbdev "ha1" 0
set sync-config enable
set gratuitous-arps enable
set ha-mgmt-status enable
config ha-mgmt-interfaces
edit 1
set interface "mgmt1"
set dst 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
set gateway 10.10.10.1
set gateway6 ::
next
end
set override enable
set priority 150
set monitor "ha1" "lacp_Inside" "lacp_outside"
set ha-direct disable
endCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Monitoring
For monitoring of the Fortigates i will use SNMP in this case. Fortinet has its own product lines that can help with this, but since most monitoring systems can use SNMP this will be my standard.
Enable SNMP
config system snmp sysinfo
set status enable
set description "FGTclu01"
set contact-info "Persons Name"
set location "Datacenter - Cluster"
endCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Configure the SNMP v2 part. I higly recommend moving to SNMPv3 over V2 for the security perspective
config system snmp community
edit 1
set name "Anchor4143"
config hosts
edit 1
set ip 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255
set ha-direct enable
next
edit 2
set ip 10.10.10.12 255.255.255.255
set ha-direct enable
next
edit 3
set ip 177.177.177.177 255.255.255.255
next
end
set query-v1-status disable
set trap-v1-status disable
set events cpu-high mem-low log-full intf-ip vpn-tun-up vpn-tun-down ha-switch ha-hb-failure ips-signature ips-anomaly av-virus av-oversize av-pattern av-fragmented fm-if-change bgp-established bgp-backward-transition ha-member-up ha-member-down ent-conf-change av-conserve av-bypass av-oversize-passed av-oversize-blocked ips-pkg-update ips-fail-open power-supply-failure faz-disconnect wc-ap-up wc-ap-down
next
endCode language: CSS (css)SNMPv3 config
config system snmp user
edit "Roster5647"
set notify-hosts 10.10.10.10
set security-level auth-priv
set auth-proto sha512
set auth-pwd xxxx
set priv-proto aes256
set priv-pwd xxxx
next
end
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Logging
Configure either fortianalyser or syslog. In this case, my focys are on the syslog part.
Enable the syslog, configure the source-ip and the server ip. In this example we are using default udp/517, but this can be changed to another port or to TCP instead.
config log syslogd setting
set status enable
set server '10.10.10.10'
set mode udp
set port 514
set facility local7
set source-ip '10.10.10.1'
set format cef
set priority default
set max-log-rate 0
set interface-select-method auto
endCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Active the events that should be logged and set the filtering and default severity level.
config log syslogd filter
set severity information
set forward-traffic enable
set local-traffic enable
set multicast-traffic enable
set sniffer-traffic enable
set ztna-traffic enable
set anomaly enable
set voip enable
end
config log eventfilter
set event enable
set system enable
set vpn enable
set user enable
set router enable
set wireless-activity enable
set wan-opt enable
set endpoint enable
set ha enable
set security-rating enable
set fortiextender enable
set connector enable
set sdwan enable
set cifs enable
set switch-controller enable
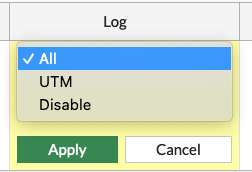
endCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Remember to enable logging on all the firewall policies. I am using ALL and not only UTM logging, since i want to know the traffic and not just the UTM events flowing through a firewall rule.
Repeat on all rules
config firewall policy
edit 1
set logtraffic all
next
endCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Or through the UI: