What is ITSM and Why Does It Matter?
Understanding IT Service Management (ITSM)
IT Service Management (ITSM) is a structured approach to designing, delivering, managing, and improving IT services within an organization. It ensures that IT services are aligned with business goals and provide value to customers. A common framework that guides ITSM is ITIL v3, which offers a structured way to handle the entire service lifecycle—from strategic planning to continuous improvement.
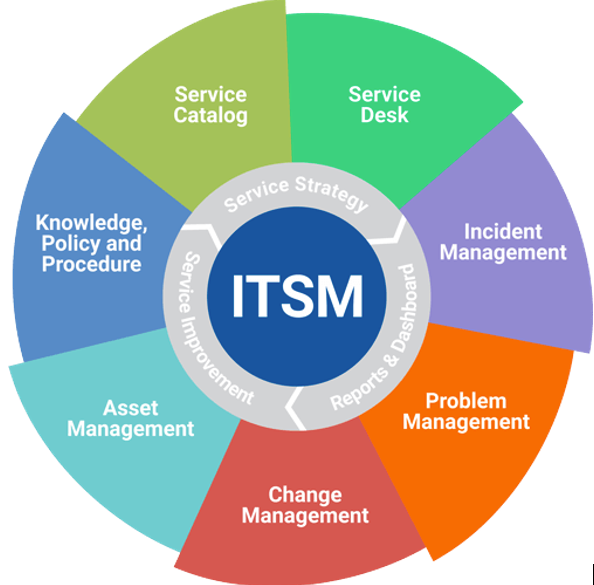
A key component of ITSM is the Service Catalog, a detailed database or portal that outlines all IT services available to users within an organization. These can include customer-facing services like email or internal services such as server hosting. This catalog provides clarity on what services are available and how users can request them. It’s also a critical tool for IT departments to manage and document services while supporting business objectives.
The Service Desk acts as the central hub for communication between IT and users. It’s the main channel for reporting incidents, service requests, or receiving IT-related support. The goal of the Service Desk is to restore normal operations as quickly as possible to minimize business disruptions.
Incident Management focuses on handling incidents that disrupt IT services, aiming to restore service as soon as possible. Effective incident management reduces downtime and maintains stable IT operations.
Meanwhile, Problem Management goes deeper by identifying and addressing the root causes of recurring issues, seeking long-term fixes to prevent future incidents. This involves root cause analysis (RCA) and implementing solutions that improve service quality over time.
Change Management is another important process in ITSM, overseeing changes to the IT infrastructure in a controlled manner to minimize risks and avoid negative impacts. This can include anything from software updates to major IT architecture changes.
Asset Management ensures that all IT assets—hardware, software, and other resources—are tracked and optimized. This process ensures assets are used efficiently, costs are controlled, and that assets comply with licensing agreements.
Knowledge Management involves collecting, organizing, and sharing knowledge within an organization. This ensures that staff have access to the information they need to make decisions and solve problems efficiently.
The Configuration Management Database (CMDB) stores details of all IT infrastructure components and how they interconnect. This database is critical for understanding the relationships between different parts of the IT system, helping to manage changes and prevent disruptions.
Why ITSM is Critical
ITSM is crucial for organizations that rely on IT services to operate. Without a structured approach, IT departments often become reactive, leading to inefficiency, dissatisfied customers, and increased costs. By implementing ITSM, organizations can align IT services with business strategy, create clear processes for resolving issues, and continuously improve services.
How Can ITSM Be Used?
ITSM can help organizations standardize processes and ensure that services are delivered efficiently. Key benefits include:
- Defining Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Everyone in the IT team knows their role in service delivery, creating clarity and accountability.
- Managing Changes Effectively: Change management processes help reduce the risk of disruptions when IT systems are updated or changed.
- Ensuring Effective Problem Resolution: ITSM helps identify and resolve problems quickly, reducing downtime and improving service quality.
- Optimizing Processes: Regular review and optimization of IT processes lead to increased efficiency.
Centralized ITSM: Efficiency at Scale
A centralized ITSM solution offers several efficiency gains:
- Improved Visibility and Control: A unified platform provides a holistic view of all IT processes and services, making management easier and more effective.
- Process Standardization: Centralized ITSM ensures that all teams follow the same processes, reducing variability and improving efficiency.
- Better Resource Utilization: By centralizing asset management, organizations can track and optimize resource usage, reducing waste.
- Cost Reduction: Standardized ITSM processes help lower operational costs by avoiding redundant tasks and improving overall efficiency.
The Power of Automation in ITSM
Automation within ITSM can drive significant improvements, including:
- Faster Response Times: Automation can handle routine tasks such as incident response without human intervention, speeding up resolution.
- Reduced Errors: Automated processes are less prone to human error, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
- Scalability: Automated systems allow IT departments to handle increasing workloads without proportionally increasing staff.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Automated monitoring tools can track performance and generate reports without delays.
Integrating Monitoring Systems with ITSM
Integrating monitoring systems with ITSM further enhances IT operations. Monitoring systems track the real-time performance and availability of IT infrastructure. When integrated with ITSM, they can automatically trigger incident or problem reports, enabling a quick and efficient response.
Key Benefits of Integration:
- Traceability: Automatic logging of incidents from monitoring systems provides full traceability, allowing IT teams to track root causes and resolutions.
- Structured Escalation: When an incident is detected, it can be escalated and documented automatically, streamlining the resolution process.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Monitoring systems can identify potential issues before they become critical, allowing for proactive management.
Real-World Use Cases for ITSM with Automation and Integration
- Automated Incident Response: When an issue is detected, an integrated ITSM and monitoring system can automatically initiate actions like restarting systems or escalating to higher support levels.
- Proactive Problem Management: By analyzing trends from monitoring data, ITSM can identify emerging issues and take preventative action.
- Escalation Automation: Critical incidents can be escalated automatically, ensuring they are addressed without delay.
- Complete Documentation and Compliance: Automated systems provide full documentation for all incidents and changes, essential for compliance with industry regulations.
In conclusion, automation and integration within ITSM not only streamline IT operations but also improve the organization’s ability to deliver reliable services and proactively address potential issues. A well-implemented ITSM solution can transform IT from a reactive cost center into a proactive, value-driving component of business success.
